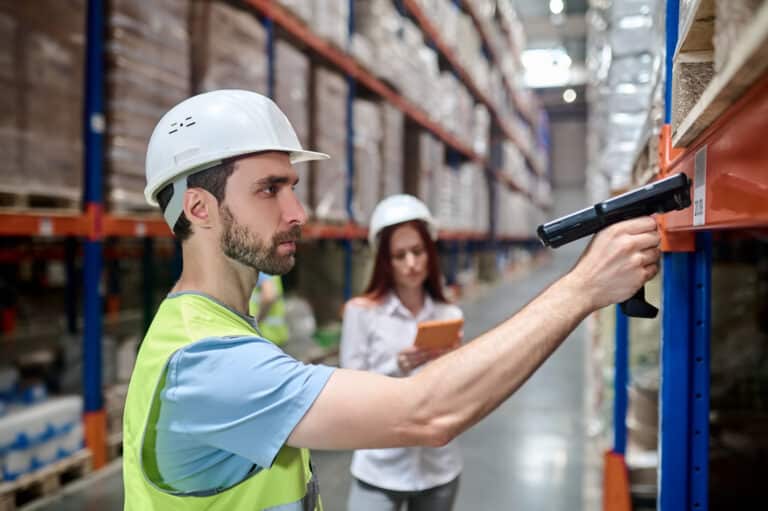
RFID technology has revolutionized the way businesses and industries track and manage their assets and inventory. With the ability to wirelessly identify and track objects using radio frequency signals, RFID systems have become an integral part of many industries, including manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and retail. However, in order to fully utilize the benefits of RFID technology, it is crucial to have the right RFID detector. In this ultimate guide, we will explore the key factors to consider when choosing an RFID detector, ensuring that you make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs.
Understanding RFID technology
Before diving into the details of choosing an RFID detector, let’s first understand the basics of RFID technology. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification and consists of two main components: RFID tags and RFID readers.
RFID tags:
These are small electronic devices that store and transmit data using radio frequency signals. They come in various forms, including adhesive labels, cards, or even embedded chips.
Also known as RFID detectors, these devices are responsible for sending and receiving radio frequency signals to communicate with RFID tags. They are equipped with antennas to capture the signals emitted by the tags and process the captured data.
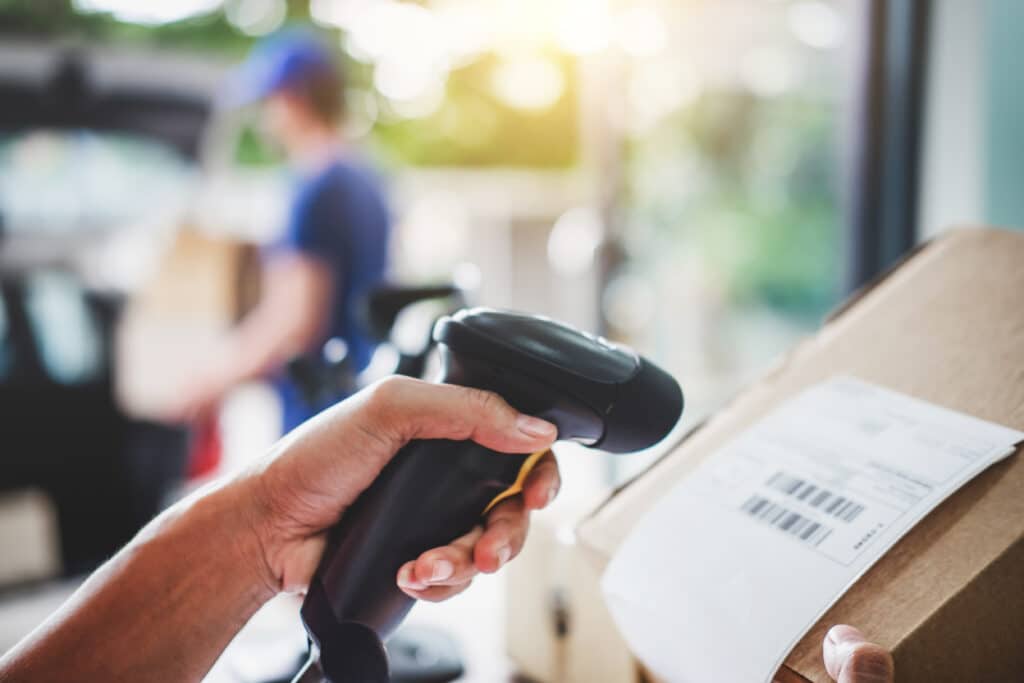

Factors to consider when choosing an RFID detector
Choosing the right RFID detector is crucial for the success of your RFID system implementation. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Frequency range: RFID technology operates on different frequency ranges, including low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF). The frequency range you choose depends on your specific application and the type of RFID tags you will be using.
- Read range: The read range refers to the distance between the RFID reader and the RFID tag. It is an important factor to consider as it determines the coverage area of your RFID system. Different RFID detectors have varying read ranges, so choose one that suits your specific needs.
- Read speed: The read speed of an RFID detector refers to how quickly it can capture and process data from RFID tags. Depending on your application, you may require a fast read speed to ensure efficient inventory management or tracking.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the RFID detector you choose is compatible with the RFID tags you plan to use. Different RFID technologies and protocols may not be compatible with each other, so it is essential to verify compatibility before making a purchase.
- Portability: Consider whether you need a portable RFID detector or a fixed one. Portable detectors are ideal for applications such as asset tracking, where mobility is essential. Fixed detectors, on the other hand, are suitable for stationary installations like access control systems.
- Connectivity: Determine the connectivity options you require for your RFID system. Some RFID detectors offer wired connections, such as Ethernet or USB, while others provide wireless connectivity options like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Ease of use: Look for an RFID detector that is user-friendly and easy to operate. A simple interface and intuitive controls can significantly reduce the learning curve and enhance the efficiency of your RFID system.
- Durability: Depending on the environment in which your RFID system will be deployed, choose a detector that can withstand various conditions like temperature extremes, moisture, and physical impacts.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of the RFID detector. Will you need to expand your RFID system in the future? Choose a detector that can accommodate future growth and can be seamlessly integrated into your existing infrastructure.
- Cost: Last but not least, consider the cost of the RFID detector. Evaluate your budget and choose a detector that offers the best value for your investment, considering both the features and performance it provides.
Conclusion
Selecting the right RFID detector is crucial for the successful implementation of an RFID system. Consider factors such as frequency range, read range, read speed, compatibility, portability, connectivity, ease of use, durability, scalability, and cost. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose an RFID detector that meets your specific needs and ensures optimal performance and efficiency in your RFID system. Embrace the power of RFID technology and unlock the full potential of asset tracking and inventory management in your industry.
FAQs
1. How far away can RFID be detected?
RFID detection range varies based on frequency and system type. In standard RFID systems, the range spans from a few inches to several feet. Specifically, UHF RFID systems operate within the 300 MHz to 960 MHz frequency range, with a typical frequency of 433 MHz. These systems can typically detect RFID tags from a distance of 25 feet or more, making them suitable for applications requiring longer-range identification and tracking capabilities.
2. How does an RFID detector prevent theft?
RFID technology serves as a theft deterrent in retail by employing plastic security tags with embedded RFID chips. These tags are attached directly to items, and when brought near a detector at the store exit, the radio frequency identification chip triggers an alarm. This immediate alert system helps prevent theft by notifying store staff promptly, allowing for quick intervention and mitigation of potential theft incidents.
3. Can RFID detect location?
Yes, RFID technology can detect locations using active tags. Standard active tags indicate an item’s presence within 300 feet of a reader. Additionally, advanced Active RFID Real-Time Location Systems (RTLS) can triangulate a tag’s location with remarkable precision, providing accuracy within 10 feet. Active Ultra-Wideband (UWB) systems take this a step further, offering location details for a tagged asset with accuracy down to a few centimeters, making them highly effective for precise asset tracking and monitoring.
4. How long does an RFID detector work?
Passive RFID tags, operating without a battery, boast a lifespan of approximately 20 years, contributing to their cost-effectiveness. These tags have a read range of 3-5 meters, making them suitable for applications like door access control, dock doors, and shop floor environments. The absence of a battery in passive RFID tags not only extends their operational life but also ensures low maintenance costs, making them a durable and efficient choice for various tracking and identification purposes.